WTF Ethers: 2. Provider
I've been revisiting ethers.js recently to refresh my understanding of the details and to write a simple tutorial called "WTF Ethers" for beginners.
Twitter: @0xAA_Science
Community: Website wtf.academy | WTF Solidity | discord | WeChat Group Application
All the code and tutorials are open-sourced on GitHub: github.com/WTFAcademy/WTF-Ethers
In this lesson, we will introduce the Provider class in ethers.js and use it to connect to an node to retrieve information from the blockchain.
Provider Class
The Provider class provides an abstraction for connecting to the Ethereum network and offers a concise and consistent interface for standard Ethereum node functionality. In ethers, the Provider class does not handle user private keys and can only read information from the blockchain, making it safer compared to web3.js.
In addition to the default provider defaultProvider mentioned previously, the most commonly used provider in ethers is jsonRpcProvider, which allows users to connect to a specific node service provider.
jsonRpcProvider
Creating an API Key for the Node Service Provider
First, you need to register and create an API Key on the website of the node service provider. In the "Tools" section of the "WTF Solidity" tutorial, we introduced the methods to create API Keys for two projects, Infura and Alchemy. You can refer to the tutorial for more information.
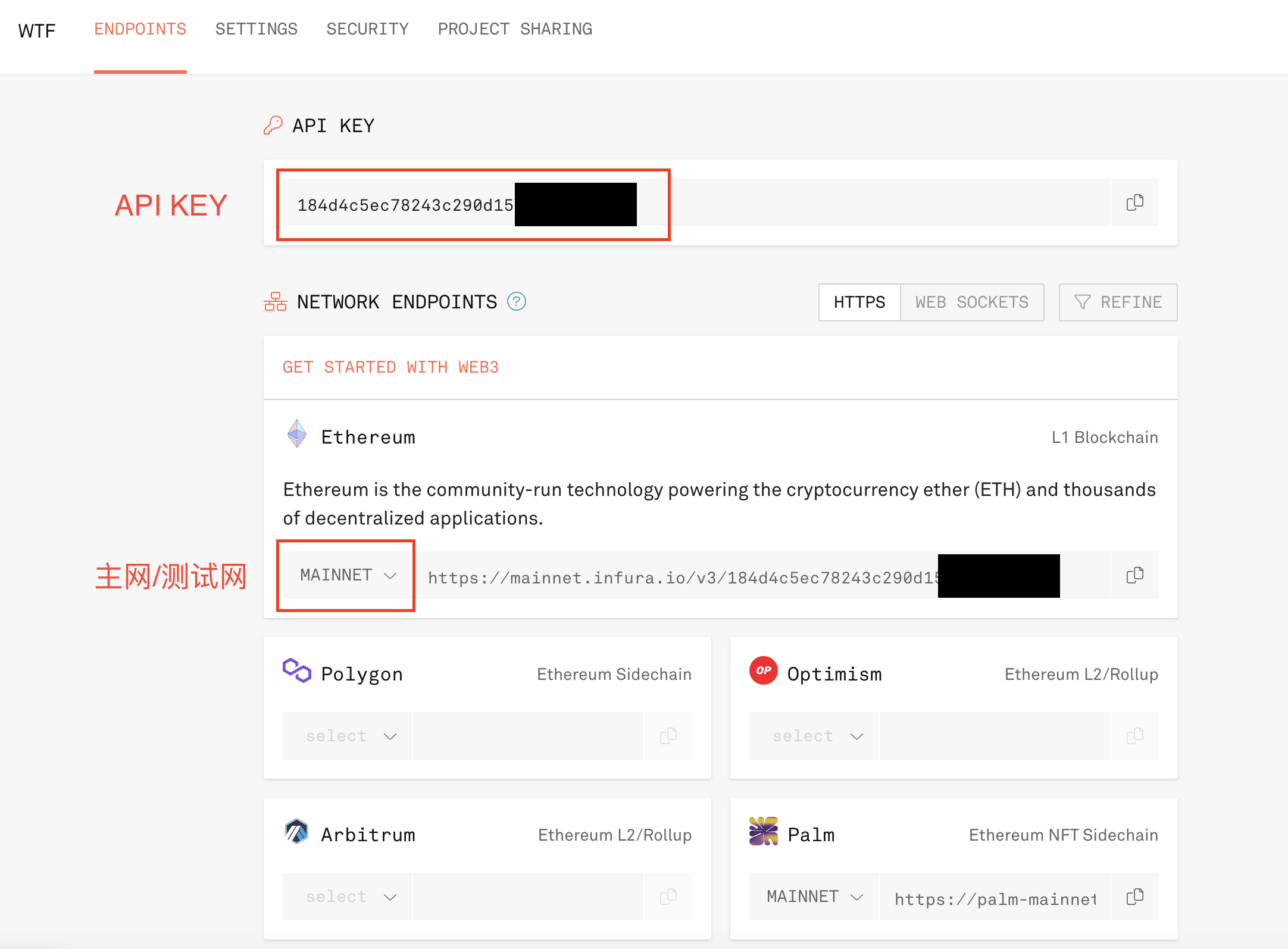
Connecting to Alchemy Node
Here, we will use Alchemy as an example. After creating the Alchemy API Key, you can create a Provider variable using the ethers.JsonRpcProvider() method, which takes the URL of the node service as a parameter.
In the following example, we create providers to connect to the ETH mainnet and the Goerli testnet:
// Connect to the Ethereum network using Alchemy's RPC node
// Prepare the alchemy API, please refer to https://github.com/AmazingAng/WTFSolidity/blob/main/Topics/Tools/TOOL04_Alchemy/readme.md
const ALCHEMY_MAINNET_URL = 'https://eth-mainnet.g.alchemy.com/v2/oKmOQKbneVkxgHZfibs-iFhIlIAl6HDN';
const ALCHEMY_GOERLI_URL = 'https://eth-goerli.alchemyapi.io/v2/GlaeWuylnNM3uuOo-SAwJxuwTdqHaY5l';
// Connect to the Ethereum mainnet
const providerETH = new ethers.JsonRpcProvider(ALCHEMY_MAINNET_URL)
// Connect to the Goerli testing network
const providerGoerli = new ethers.JsonRpcProvider(ALCHEMY_GOERLI_URL)
Using the Provider to Retrieve Blockchain Data
The Provider class provides convenient methods to retrieve data from the blockchain:
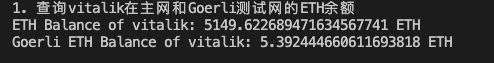
1. Use the getBalance() function to retrieve the ETH balance of Vitalik on the mainnet and the Goerli testnet:
// 1. Retrieve the ETH balance of Vitalik on the mainnet and the Goerli testnet
console.log("1. Retrieving the ETH balance of Vitalik on the mainnet and the Goerli testnet");
const balance = await providerETH.getBalance(`vitalik.eth`);
const balanceGoerli = await providerGoerli.getBalance(`vitalik.eth`);
// Output the balances on the console (mainnet)
console.log(`ETH Balance of Vitalik: ${ethers.formatEther(balance)} ETH`);
// Output the Goerli testnet ETH balance
console.log(`Goerli ETH Balance of Vitalik: ${ethers.formatEther(balanceGoerli)} ETH`);
2. Use the getNetwork() function to check which chain the provider is connected to. homestead represents the ETH mainnet:
// 2. Check which chain the provider is connected to
console.log("\n2. Checking which chain the provider is connected to")
const network = await providerETH.getNetwork();
console.log(network.toJSON());
In ethers v6, the above code cannot directly
console.log()thenetworkobject. Refer to the discussion-3977 for the specific reason.
3. Use the getBlockNumber() function to retrieve the current block number:
// 3. Retrieve the current block number
console.log("\n3. Retrieving the current block number")
const blockNumber = await providerETH.getBlockNumber();
console.log(blockNumber);

4. Use the getTransactionCount() function to retrieve the transaction count of a wallet address.
// 4. Retrieve the transaction count of Vitalik's wallet
console.log("\n4. Retrieving the transaction count of Vitalik's wallet")
const txCount = await providerETH.getTransactionCount("vitalik.eth");
console.log(txCount);
5. Use the getFeeData() function to retrieve the current recommended gas settings, which are returned as bigint.
// 5. Retrieve the current recommended gas settings
console.log("\n5. Retrieving the current recommended gas settings")
const feeData = await providerETH.getFeeData();
console.log(feeData);

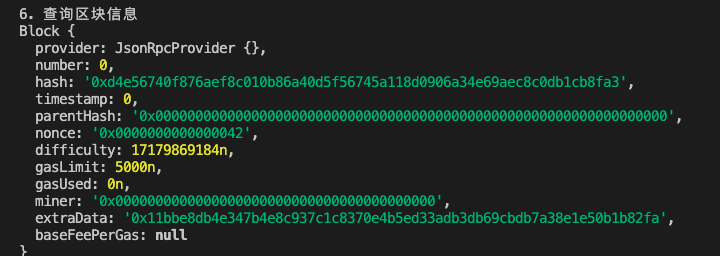
6. Use the getBlock() function to retrieve information about a specific block. The parameter is the block number:
// 6. Retrieve information about a specific block
console.log("\n6. Retrieving information about a specific block")
const block = await providerETH.getBlock(0);
console.log(block);
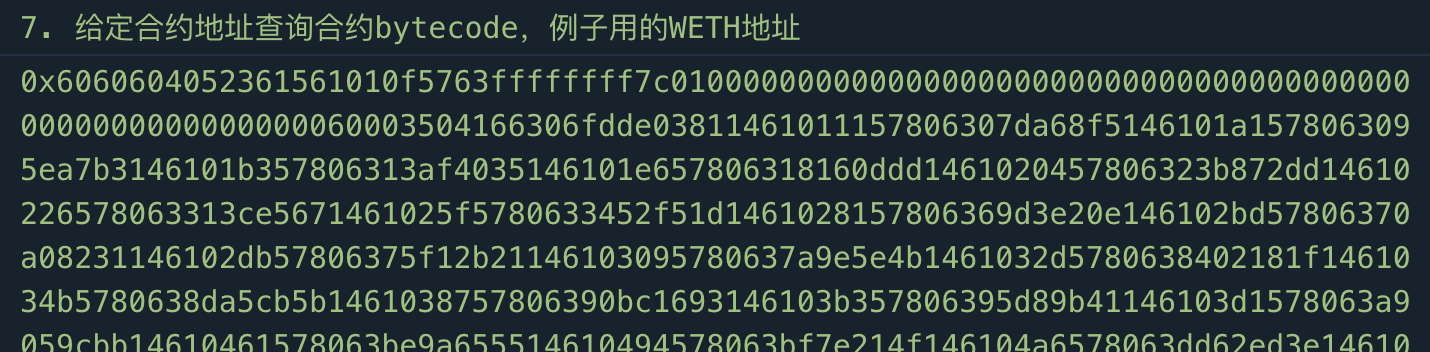
7. Use the getCode() function to retrieve the bytecode of a contract at a specific address. In the example below, we use the contract address of WETH on the mainnet:
// 7. Retrieve the bytecode of a contract at a specific address, using the contract address of WETH on the mainnet as an example
console.log("\n7. Retrieving the bytecode of a contract at a specific address, using the contract address of WETH on the mainnet as an example")
const code = await providerETH.getCode("0xc778417e063141139fce010982780140aa0cd5ab");
console.log(code);
Summary
In this lesson, we introduced the Provider class of ethers.js and create a jsonRpcProvider with Alchemy's node API key to read on-chain information from the ETH main network and Goerli test network.